1 容器集简单介绍
java.util包下面的容器集主要有两种,一种是Collection接口下面的List和Set,一种是Map,
大致结构如下:
Collection
- List
- LinkedList
- ArrayList
- Vector
- Set
- HashSet
- TreeSet
- LinkedSet
Map
- Hashtable
- HashMap
- WeakHashMap
2 同步容器
同步容器也叫线程安全容器,是通过syncrhoized关键字对线程不安全的操作进行加锁来保证线程安全的
其中同步容器主要包括:
1.Vector、Stack、HashTable
2.Collections 工具类中提供的同步集合类
Collections类是一个工具类,相当于Arrays类对于Array的支持,Collections类中提供了大量对集合或者容器进行排序、查找的方法。它还提供了几个静态方法来创建同步容器类:
3 并发容器
java.util.concurrent提供了多种线程安全容器,大多数是使用系统底层技术实现的线程安全,也叫并发容器,类似native。Java8中使用CAS。
4 案例讲解
这里主要介绍一些常见的同步容器和并发容器,通过案例输出结果对比进行介绍
我大致分为了三类Map/Set,List,Queue来进行讲解,但一个Map/Set,只介绍了Map,因为在java的设计中,Set就是Map,说白了就是只有Key没有Value的Map,好了,现在开始进入正题
4.1 Map/Set
代码中new了三个Map,HashTable,ConcurrentHashMap,ConcurrentSkipListMap比较每个map的运行效率,起100个线程向map中存放10000条随机数,并通过门闩CountDownLatch控制运行状态,输出运行时间
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
package com.bernardlowe.concurrent.t06;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentSkipListMap;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
public class Test_01_ConcurrentMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Map<String, String> map = new Hashtable<>();
final Random r = new Random();
Thread[] array = new Thread[100];
final CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(array.length);
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i = 0; i < array.length; i++){
array[i] = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for(int j = 0; j < 10000; j++){
map.put("key"+r.nextInt(100000000), "value"+r.nextInt(100000));
}
latch.countDown();
}
});
}
for(Thread t : array){
t.start();
}
try {
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("执行时间为 : " + (end-begin) + "毫秒!");
}
}
|
Hashtable结果:
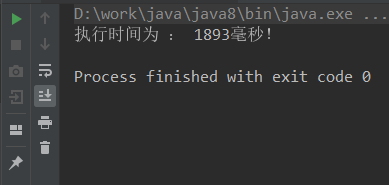
ConcurrentHashMap结果:
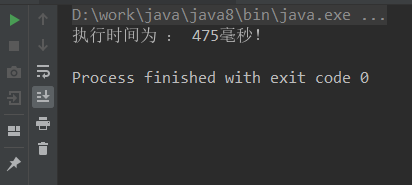
ConcurrentSkipListMap结果:
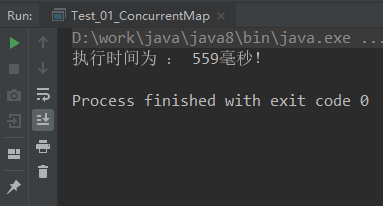
ConcurrentHashMap的底层是哈希实现的同步Map(Set)
ConcurrentSkipListMap内部是SkipList(跳表)结构实现的非阻塞读/写/删除 的 Map,它的value是有序存储的, 而且其内部是由纵横链表组成,在JDK1.8中,ConcurrentHashMap的性能和存储空间要优于ConcurrentSkipListMap
为了让测试数据结果对比更加直观,我这里故意将生成的随机数调的比较大。这里需要注意一下,在测试的时候,如果机器性能比较好,可能结果会出现误差,因为System.currentTimeMillis(),这个方法调用了个native方法,获取的时间精度会依赖于操作系统的实现机制,具体为什么,可以看看这篇文章http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_6b8bd9d80101fe8t.html。但我按照文档的办法将System.currentTimeMillis()改为System.nanoTime(),发现并没有解决这个问题,可能是因为并没有达到纳秒级别吧。
4.2 List
下面代码与4.1的代码类似,也是new了三个List,ArrayList,Vector,CopyOnWriteArrayList,起100个线程向map中存放1000条随机数,并通过门闩CountDownLatch控制运行状态,输出运行时间和最后list的的长度。由于ArrayList是线程不安全,在多线程执行的时候,需要try{}catch{},否则会因为数组越界而报错,因为ArrayList底层是一个长度动态扩展的数组
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
package com.bernardlowe.concurrent.t06;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Vector;
import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
public class Test_02_CopyOnWriteList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
final Random r = new Random();
Thread[] array = new Thread[100];
final CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(array.length);
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i = 0; i < array.length; i++){
array[i] = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for(int j = 0; j < 1000; j++){
try {
list.add("value" + r.nextInt(100000));
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
latch.countDown();
}
});
}
for(Thread t : array){
t.start();
}
try {
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("执行时间为 : " + (end-begin) + "毫秒!");
System.out.println("List.size() : " + list.size());
}
}
|
ArrayList结果:因为ArrayList是线程不安全的,所以在多线程环境中,可能会丢失数据
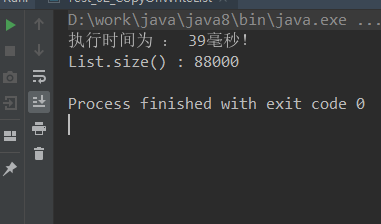
Vector结果:
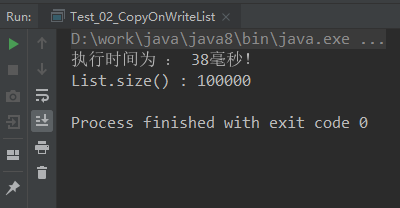
CopyOnWriteArrayList结果:
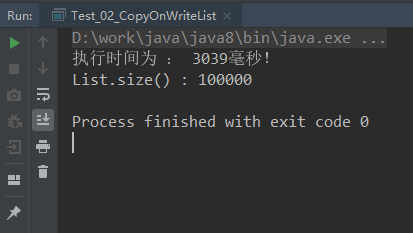
CopyOnWriteArrayList是读写分离的,写时复制出一个新的数组,完成插入、修改或者移除操作后将新数组赋值给array,读取时直接读取最新的数组,所以在写操作时,效率非常低(虽然写比较慢,但它在删除数组头和尾还是很快的)
从上面三个结果可以看出,CopyOnWriteArrayList虽然保证了线程安全,但它的写操作效率太低了,但相比Vector,并发安全且性能比Vector好,Vector是增删改查方法都加了synchronized,保证同步,但是每个方法执行的时候都要去获得锁,性能就会大大下降,而CopyOnWriteArrayList 只是在增删改上加锁,但是读不加锁,在读方面的性能就好于Vector,CopyOnWriteArrayList支持读多写少的并发情况,所以CopyOnWriteArrayList是不会存在脏读问题的
4.3 Queue
常用阻塞队列
- ArrayBlockingQueue: 一个数组结构组成的有界阻塞队列,按照先进先出原则,要求设定初始大小
- LinkedBlockingQueue: 一个由链表结构组成的有界队列,按照先进先出的原则,可以不设置初始大小,默认为Integer.Max_Value(0x7fffffff)
ArrayBlockingQueue只有一个锁,LinkedBlockingQueue用了两个锁
- PriorityBlockingQueue:一个支持优先级排序的无界阻塞队列,默认按照自然顺序,要么实现compareTo()方法,指定构造方法Comparator
- DelayQueue: 一个使用优先级队列实现的无界阻塞队列
- SynchronousQueue: 一个不存储元素的阻塞队列
- LinkedTransferQueue:一个又链表结构组成的无界阻塞队列
- LinkedBlockDeque:一个由链表结构组成的双向阻塞队列,可以从队列的头和尾部插入和移除元素,实现工作的密取
4.3.1 ConcurrentLinkedQueue
基础链表同步队列
peek() -> 查看queue中的首数据
poll() -> 获取queue中的首数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
package com.bernardlowe.concurrent.t06;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedQueue;
public class Test_03_ConcurrentLinkedQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<String> queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
queue.offer("value" + i);
}
System.out.println(queue);
System.out.println(queue.size());
System.out.println("首数据 " + queue.peek());
System.out.println("队列长度 "+ queue.size());
System.out.println("===================");
System.out.println("首数据 " + queue.peek());
System.out.println("队列长度 "+ queue.size());
}
}
|
结果:
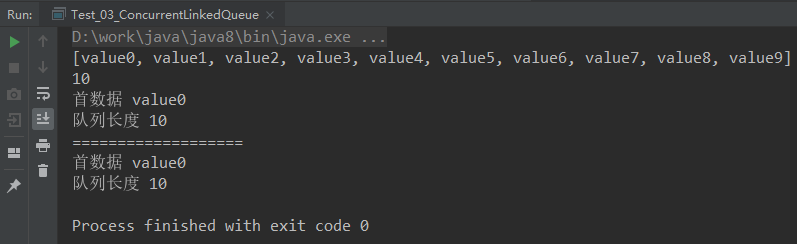
4.3.2 阻塞队列LinkedBlockingQueue
阻塞队列,队列容量不足自动阻塞,队列容量为0自动阻塞。
put & take - 自动阻塞
put自动阻塞, 队列容量满后,自动阻塞
take自动阻塞方法, 队列容量为0后,自动阻塞
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
|
package com.bernardlowe.concurrent.t06;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class Test_04_LinkedBlockingQueue {
final BlockingQueue<String> queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
final Random r = new Random();
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Test_04_LinkedBlockingQueue t = new Test_04_LinkedBlockingQueue();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
try {
t.queue.put("value"+t.r.nextInt(1000));
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}, "producer").start();
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +
" - " + t.queue.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}, "consumer"+i).start();
}
}
}
|
结果:
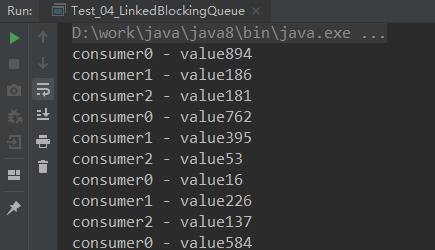
结果就是一个简单的生产者消费者
4.3.3 BlockingQueue
底层数组实现的有界队列,当容量不足的时候,有阻塞能力,根据调用API(add/put/offer)不同,有不同特性
这里主要介绍三个api方法add,put,offer
- add方法在容量不足的时候,抛出异常。
- put方法在容量不足的时候,阻塞等待。
- offer方法
单参数offer方法,不阻塞。容量不足的时候,返回false。当前新增数据操作放弃。
三参数offer方法(offer(value,times,timeunit)),容量不足的时候,阻塞times时长(单位为timeunit),如果在阻塞时长内,有容量空闲,新增数据返回true。如果阻塞时长范围内,无容量空闲,放弃新增数据,返回false。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
package com.bernardlowe.concurrent.t06;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class Test_05_ArrayBlockingQueue {
final BlockingQueue<String> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Test_05_ArrayBlockingQueue t = new Test_05_ArrayBlockingQueue();
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
System.out.println("add method : " + t.queue.add("value"+i));
}
System.out.println(t.queue);
}
}
|
add方法结果:容量不足的时候,抛出异常
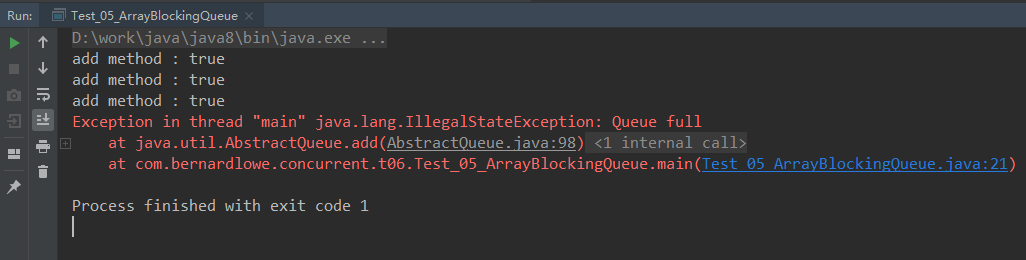
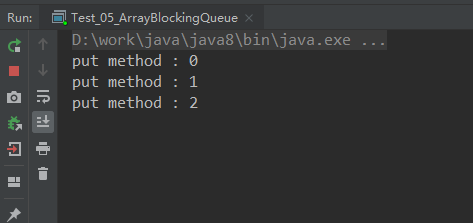
put方法结果:容量不足的时候,阻塞等待
单/多参数offer方法结果:
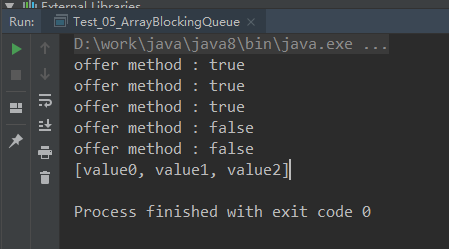
单参数offer:容量不足,直接返回结果,不阻塞
多参数offer:容量不足,阻塞
4.3.4 延时队列DelayQueue
延时队列。根据比较机制,实现自定义处理顺序的队列。常用于定时任务。
如:定时关机。
具体示例代码如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
|
package com.bernardlowe.concurrent.t06;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Delayed;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class Test_06_DelayQueue {
static BlockingQueue<MyTask_06> queue = new DelayQueue<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
long value = System.currentTimeMillis();
MyTask_06 task1 = new MyTask_06(value + 2000);
MyTask_06 task2 = new MyTask_06(value + 1000);
MyTask_06 task3 = new MyTask_06(value + 3000);
MyTask_06 task4 = new MyTask_06(value + 2500);
MyTask_06 task5 = new MyTask_06(value + 1500);
queue.put(task1);
queue.put(task2);
queue.put(task3);
queue.put(task4);
queue.put(task5);
System.out.println(queue);
System.out.println(value);
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
System.out.println(queue.take());
}
}
}
class MyTask_06 implements Delayed {
private long compareValue;
public MyTask_06(long compareValue){
this.compareValue = compareValue;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Delayed o) {
return (int)(this.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) - o.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
}
@Override
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
return unit.convert(compareValue - System.currentTimeMillis(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return "Task compare value is : " + this.compareValue;
}
}
|
结果:
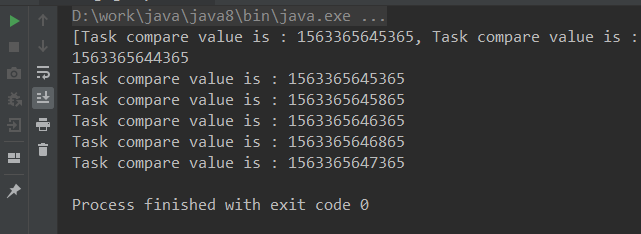
4.3.5 转移队列LinkedTransferQueue
这里主要是两个方法的区别,add和transfer
- add - 队列会保存数据,不做阻塞等待。
- transfer - 是TransferQueue的特有方法。必须有消费者(take()方法的调用者)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
|
package com.bernardlowe.concurrent.t06;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedTransferQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.TransferQueue;
public class Test_07_TransferQueue {
TransferQueue<String> queue = new LinkedTransferQueue<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Test_07_TransferQueue t = new Test_07_TransferQueue();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
t.queue.transfer("test string");
System.out.println("add ok");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " thread begin " );
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " - " + t.queue.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "output thread").start();
}
}
|
举个例子,transfer()就相当与手机打电话,当A给B打电话,B必须接收到电话信号接听才能进行通话,否则A会一直等待
add()就相当于A给B发短信,短信已经存到了运营商那边,等待B接收,不管发短信时B是否在线
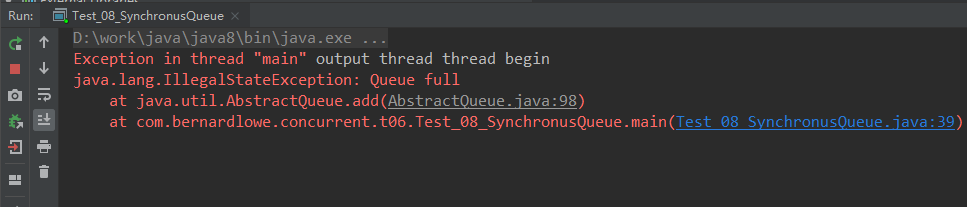
4.3.6 SynchronousQueue
该队列一个容量为0的队列,是一个特殊的TransferQueue,它和TransferQueue很像,但这个队列必须要有消费线程才行
又两个方法add,put
add方法,无阻塞。若没有消费线程阻塞等待数据,则抛出异常。
put方法,有阻塞。若没有消费线程阻塞等待数据,则阻塞。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
|
package com.bernardlowe.concurrent.t06;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class Test_08_SynchronusQueue {
BlockingQueue<String> queue = new SynchronousQueue<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Test_08_SynchronusQueue t = new Test_08_SynchronusQueue();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " thread begin " );
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " - " + t.queue.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "output thread").start();
try {
t.queue.put("test put");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " queue size : " + t.queue.size());
}
}
|
将t.queue.add("test add");的注释打开,t.queue.put("test put");加上注释
add方法异常结果: 因为它是一个容量为0的队列
更多精彩内容:mrxccc